1.
This is a drawing of the external surface of the brain; I labeled the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem.
This is a drawing of the external surface of the brain; I labeled the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem.
 |
| Red: brain stem Green: cerebellum Yellow: cerebrum |
Structure
|
Function
|
Cerebrum
|
Integrates information that it receives and is responsible for complex sensory and neural functions
|
Cerebellum
|
Motor control and coordination
|
Brain Stem
|
Necessary functions, like heart rate and breathing
|
3. In a neuron, the fatty myelin provides insulation that increases the speed of impulses through these myelinated neurons.
4.
4.
 |
| This is a drawing of the inside of the brain (if the brain is cut longitudinally). The pons, hypothalamus, optic nerve, thalamus, medulla oblongata, midbrain, and corpus callosum are labeled. |
 |
| Blue: hypothalamus Red: medulla oblongata Green: pons Yellow: thalamus |
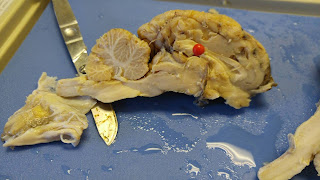 |
| Red: corpus callosum |
 |
| Green: optic nerve |
5.
Structure
|
Function
|
Thalamus
|
Sorts data and sends it where it needs to go; “post office”
|
Optic Nerve
|
Receives nerve impulses from retina and sends to brain for interpretation
|
Medulla Oblongata
|
Part of the brain stem that controls heart and lung functions
|
Pons
|
Controls respiration, sleep, swallowing, and other functions
|
Midbrain
|
Controls vision, motor control, hearing, and sleep
|
Corpus Callosum
|
Nerve fibers that connect the two hemispheres of the brain and relay information between the two
|
Hypothalamus
|
Controls regulation and homeostasis
|
6.
Relate and Review:
- In this lab, we identified the structures of the brain through several simple cuts and also learned their functions. First, we identified the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem from just looking at the outside of the brain. Next, we cut the brain longitudinally in half and saw the gray and white matter. Then, we identified the thalamus, optic nerve, medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, corpus callosum, and hypothalamus from looking at the medial plane of the brain. Next, we then made a cross sectional cut of the cerebrum, which allowed us to see the gray and white matter more clearly. In this lab, I thought that the dissection actually was very similar to the diagrams in textbooks. Something that surprised me was that although the hypothalamus is so small in real life, it controls something very important, like homeostasis.
 |
| Half of the cerebrum (cut hamburger-style). |
 |
| The gray and white matter of the brain are labeled. |
- In this lab, we identified the structures of the brain through several simple cuts and also learned their functions. First, we identified the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem from just looking at the outside of the brain. Next, we cut the brain longitudinally in half and saw the gray and white matter. Then, we identified the thalamus, optic nerve, medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, corpus callosum, and hypothalamus from looking at the medial plane of the brain. Next, we then made a cross sectional cut of the cerebrum, which allowed us to see the gray and white matter more clearly. In this lab, I thought that the dissection actually was very similar to the diagrams in textbooks. Something that surprised me was that although the hypothalamus is so small in real life, it controls something very important, like homeostasis.

No comments:
Post a Comment